Leave Your Message
In the rapidly evolving world of manufacturing, ultrasonic welding has emerged as a pivotal technology, significantly enhancing the efficiency and quality of assembly processes. Central to this innovation are "Transducers Ultrasonic Welder," which play a crucial role in converting electrical energy into high-frequency mechanical energy. As industry expert Dr. Emily Carter emphasizes, "The effectiveness of ultrasonic welding largely depends on the precision and performance of the transducers; they are the heartbeat of the system." This highlights the importance of selecting the right transducer to optimize welding outcomes and ensure reliability across various applications.
As we look towards 2025, staying informed about the latest advancements in transducer technology is essential for manufacturers aiming to maintain a competitive edge. The development of new materials, enhanced design techniques, and improved signal processing are all shaping the future landscape of Transducers Ultrasonic Welder. Understanding these advancements will equip professionals in the field with the knowledge necessary to leverage ultrasonic welding technology effectively, ultimately driving innovation and productivity in their respective industries.
With the increasing demand for high-performance welding solutions, exploring the top transducer options becomes imperative for engineers and production managers alike. This guide aims to provide key insights into the best transducers available in 2025, helping stakeholders make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and enhance their manufacturing capabilities.
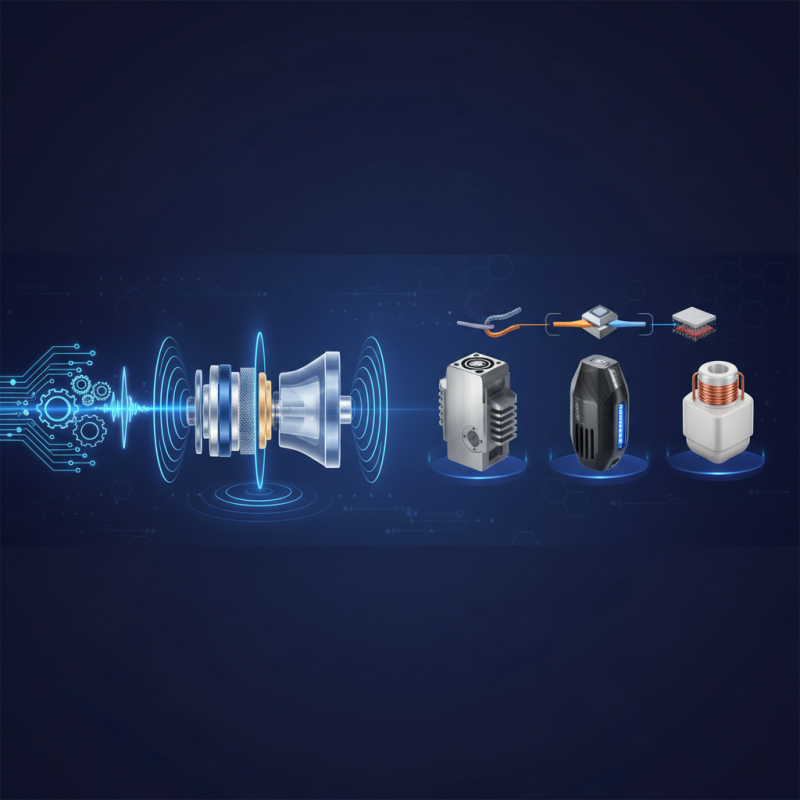


When selecting transducers for ultrasonic welders, understanding their key features is crucial for optimizing performance. The efficiency and reliability of ultrasonic welding processes largely depend on the specifications of the transducers used. According to a recent industry report, high-frequency transducers operating between 20 kHz to 40 kHz are most commonly utilized, as they provide superior bonding quality and reduced cycle times. Factors such as frequency stability, amplitude consistency, and thermal management capabilities are essential to ensure that the transducers deliver the necessary power without overheating or compromising the integrity of the weld.
Another critical aspect to consider is the power rating of transducers, which typically ranges from 100 to 500 watts. The power output directly impacts the welding speed and the thickness of materials that can be effectively processed. An increase in power rating can lead to higher energy transfer efficiency, resulting in improved joint strength. Additionally, compatibility with various materials such as plastics, metals, and composites enhances the versatility of the welder. Industry surveys indicate that manufacturers are increasingly prioritizing the development of transducers with advanced piezoelectric materials, which offer higher efficiency and durability over traditional options, thereby expanding their range of applications in the market.
Ultrasonic welding is a critical process in various industries, relying heavily on efficient and robust transducers that convert electrical energy into mechanical vibrations. One of the key choices in this area is between piezoelectric and capacitive transducers, each offering distinct advantages tailored to specific applications. Piezoelectric transducers are renowned for their high-frequency capabilities and precise control, operating effectively in a range of materials, including plastics and metals. According to a report by Market Research Future, the global ultrasonic transducer market is projected to reach USD 1.6 billion by 2025, driven primarily by the advancements in piezoelectric technology.
On the other hand, capacitive transducers present an alternative that is often less complex in design and can be more cost-effective over time. While they may not match the high frequency output of their piezoelectric counterparts, capacitive options can provide sufficient energy for medium-range applications, particularly in thin materials. Recent studies indicate that capacitive transducers can handle variations in power supply more gracefully, making them suitable for uses where operational consistency is key. As industries continue to innovate and adopt ultrasonic welding, understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each transducer type will be essential for optimizing production processes and achieving desired results.
When selecting transducers for ultrasonic welders, understanding performance metrics such as frequency and power ratings is essential. Frequency, measured in kilohertz (kHz), indicates how many cycles the ultrasonic wave completes in one second. Different applications require different frequencies; for example, lower frequencies (20 kHz - 40 kHz) are generally better suited for bonding thicker materials, while higher frequencies (above 40 kHz) are ideal for finer, more precise tasks. The right frequency can significantly impact the effectiveness of the welding process, ensuring optimal energy transmission and a strong bond.
Power ratings denote the maximum output capacity of the transducer and are critical for assessing its suitability for specific welding applications. Higher power ratings typically mean that the transducer can deliver more energy to facilitate the welding process, thereby allowing for better penetration and material bonding. However, it is crucial to match the power rating to the type of materials being welded and the welding environment, as excessive power can lead to material damage or inefficient bonding. Understanding these metrics is vital for achieving effective and reliable ultrasonic welding results, paving the way for informed choices in transducer selection.
| Model | Frequency (kHz) | Power Rating (Watts) | Material | Weight (kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model A | 20 | 200 | Titanium | 1.5 |
| Model B | 26 | 150 | Aluminum | 1.2 |
| Model C | 30 | 300 | Steel | 2.0 |
| Model D | 15 | 180 | Ceramic | 1.3 |
| Model E | 22 | 250 | Plastic | 1.0 |
When selecting materials for ultrasonic welders, it is crucial to prioritize durability and efficiency to ensure optimal performance. The choice of transducer materials directly influences the lifespan of the welding equipment and the quality of the welds produced. Generally, high-strength alloys and composites are preferred for their resistance to wear and fatigue. These materials can withstand the mechanical stresses imposed during ultrasonic welding, minimizing the risk of failure and maintenance costs.
In addition to mechanical strength, the thermal stability of the materials should be considered. During the welding process, high-frequency vibrations generate significant heat, which can compromise the integrity of weaker materials. Thus, materials that maintain their properties under varying temperatures are ideal for transducers. Furthermore, the acoustic impedance of selected materials plays a vital role in ensuring efficient energy transfer, thereby improving the overall efficacy of the welding process. By carefully considering these factors, manufacturers can enhance both the durability and efficiency of their ultrasonic welding systems.
As we look towards 2025, the advancements in ultrasonic transducer technology are set to shape the future of welding applications significantly. The ultrasonic welding industry is expected to witness a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 6% from 2023 to 2028, driven by the increasing demand for high-precision manufacturing in sectors such as automotive, electronics, and medical devices. Innovations in transducer materials, including piezoelectric ceramics and composite materials, are leading to enhanced performance metrics, including higher efficiency and reduced energy consumption.
One of the key trends anticipated is the integration of smart technology within ultrasonic transducers. This involves the incorporation of IoT capabilities that allow for real-time monitoring and data analytics, facilitating proactive maintenance and optimizing welding processes. Reports indicate that implementing such smart systems can reduce downtime by up to 30%, further solidifying the demand for advanced transducer solutions.
Additionally, the design of transducers is evolving towards miniaturization and increased versatility. New fabrication techniques, like additive manufacturing, are being explored to create compact transducers that can perform multiple functions, thereby providing manufacturers with more flexible production capabilities. This trend not only aligns with the growing emphasis on sustainability but also promises to enhance the precision and consistency of welds across various applications. As innovations continue to transform the ultrasonic welding landscape, staying informed about these trends will be crucial for industry players aiming to maintain a competitive edge.