Leave Your Message
In the realm of advanced manufacturing and assembly processes, the "Small Ultrasonic Welder" has emerged as a pivotal tool for both DIY enthusiasts and industrial applications. This cutting-edge technology employs high-frequency ultrasonic vibrations to create strong molecular bonds between materials, ensuring durability and precision. According to Dr. Emily Zhang, a leading expert in ultrasonic welding technology, "The Small Ultrasonic Welder revolutionizes how we approach material joining, offering a cleaner and more efficient alternative to traditional welding methods."
As industries increasingly demand smaller and more versatile tools that can handle delicate components, the Small Ultrasonic Welder rises to the occasion. It is particularly advantageous in sectors such as electronics, automotive, and medical device manufacturing, where precision and reliability are paramount. Dr. Zhang further emphasizes, "Its compact design does not compromise its power, making it an indispensable asset for getting the job done right."
This introduction will delve further into the working principles, applications, and benefits of the Small Ultrasonic Welder, highlighting how it can transform your projects into successful outcomes through innovative material joining techniques. Whether you're a professional engineer or a hobbyist, understanding this technology could enhance your productivity and expand your capabilities in various projects.
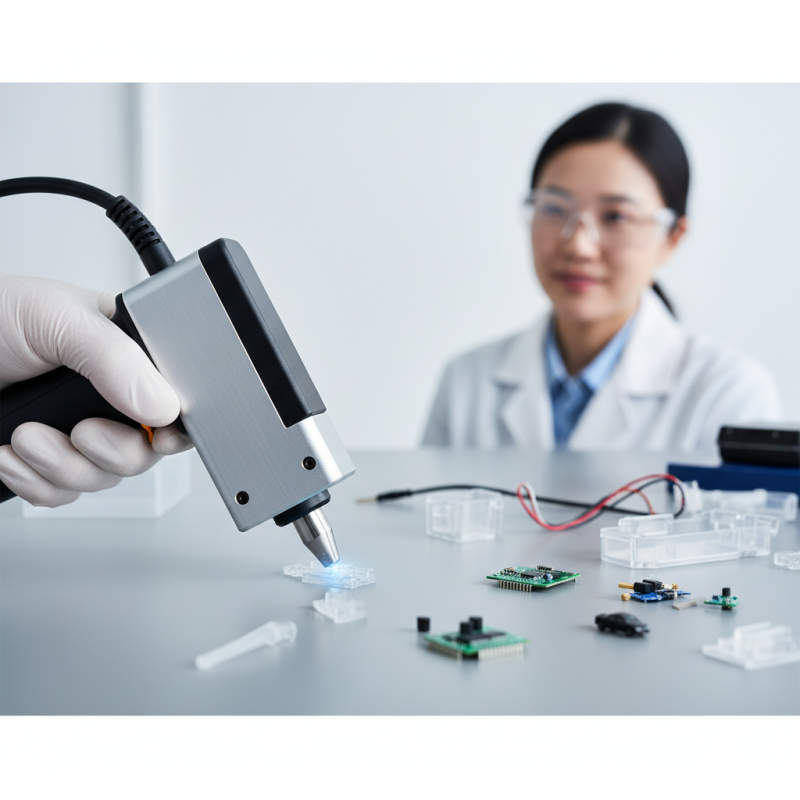

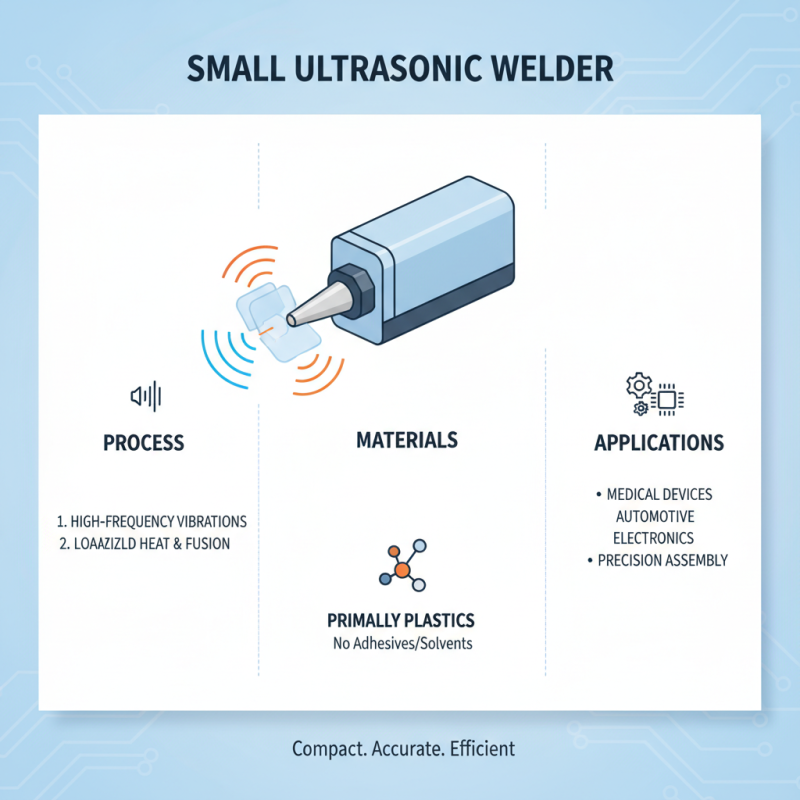
A small ultrasonic welder is a specialized device designed to join materials, commonly plastics, through the application of high-frequency ultrasonic vibrations. These vibrations generate localized heat at the interface of the materials being bonded, allowing them to melt and fuse together without the need for additional adhesives or solvents. The compact size of these welders makes them particularly useful in precision applications, such as in the medical device, automotive, and electronics industries, where space is often at a premium and accuracy is essential.
According to industry reports, the global ultrasonic welding market is expected to grow significantly, projected to reach USD 1.2 billion by 2025, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 5.6%. The increasing demand for lightweight and energy-efficient products drives innovation in ultrasonic welding technology. Additionally, small ultrasonic welders are lauded for their efficiency, offering fast cycle times and reduced thermal damage to sensitive components compared to traditional welding methods. This makes them an ideal choice for manufacturers looking to streamline their production processes while maintaining high quality in assembly operations.
Small ultrasonic welders are becoming increasingly popular in various industries due to their efficiency and precision in joining different materials. Understanding the key components of these machines can significantly enhance the effectiveness of your projects. The primary elements of a small ultrasonic welder include the ultrasonic generator, transducer, booster, and sonotrode. Each of these parts plays a critical role in converting electrical energy into mechanical vibrations that can fuse materials.
The ultrasonic generator acts as the power source, converting standard electrical power into high-frequency ultrasonic energy. This energy is then transmitted to the transducer, which transforms it into mechanical vibrations. The booster amplifies these vibrations, while the sonotrode, or welding horn, further focuses this energy onto the materials being joined. According to a report by Markets and Markets, the ultrasonic welding equipment market is projected to reach $1.4 billion by 2025, indicating the growing reliance on this technology in sectors such as automotive, electronics, and medical devices.
Moreover, the ability of ultrasonic welders to work with both thermoplastics and metals makes them invaluable across various applications. The high-speed nature of the process, coupled with reduced energy consumption, aligns with modern manufacturing goals of efficiency and sustainability. A 2021 industry analysis revealed that ultrasonic welding significantly reduces cycle times and improves joint strength, further supporting its adoption in an array of projects. Understanding these components allows users to optimize their use of small ultrasonic welders, leading to better outcomes in their production processes.
Ultrasonic welding is a highly efficient joining process primarily utilized for thermoplastics and thin metals. It employs high-frequency ultrasonic vibrations to create localized heat, which melts the materials at the interface. During the welding process, a transducer transforms electrical energy into mechanical vibration, which is then amplified and focused onto the workpieces. As the ultrasonic energy is applied under pressure, the friction generated at the contact surface causes the materials to fuse together in mere seconds, resulting in strong and reliable joints without the need for adhesives or additional fasteners.
According to a report by Global Industry Analysts, the ultrasonic welding market is expected to reach USD 7.7 billion by 2027, driven by the growing demand for lightweight and durable components in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and medical devices. This technology is particularly advantageous for micro-welding applications due to its precision and ability to produce clean welds, even on complex geometries.
Moreover, as industries continue to prioritize automation and efficiency, ultrasonic welding stands out for its fast cycle times, often completing welds in less than a minute, significantly boosting production rates. With its low energy consumption and minimal waste generation, ultrasonic welding is not only a cost-effective solution but also an environmentally friendly manufacturing process.
Small ultrasonic welders are incredibly versatile tools that find applications across a myriad of industries. In the medical sector, they are used to join thermoplastic materials in the production of medical devices, ensuring strong and reliable seams that meet stringent industry standards. Their precision minimizes the risk of contamination and maintains the integrity of sensitive components, which is crucial for the safety and efficacy of medical products.
In the automotive industry, small ultrasonic welders are employed to assemble various plastic parts, such as interior components and electronic housings. The speed and efficiency of ultrasonic welding allow for rapid production while ensuring strong joint integrity, which is essential for vehicle durability and performance. Additionally, these welders are increasingly used in the consumer electronics sector, where they facilitate the assembly of complex devices like smartphones and laptops, providing a clean and efficient bonding method without the need for adhesives or additional fasteners. Through their wide-ranging applications, small ultrasonic welders are transforming manufacturing processes and enhancing product quality across different fields.
When selecting the right small ultrasonic welder for your projects, it's essential to consider several key factors that can significantly influence the effectiveness and efficiency of your welding tasks. Ultrasonic welding operates at high frequencies, typically ranging from 20 kHz to 40 kHz. The choice of frequency impacts the weld quality, particularly with different materials. For example, studies have shown that a frequency of around 20 kHz is more suitable for thicker plastics, while 40 kHz works better for thinner materials. Understanding your project's specific requirements will help determine the optimal frequency for achieving the best results.
Another crucial aspect is the power output of the ultrasonic welder. Research indicates that power settings can vary from 100 watts to several kilowatts, directly correlating with the depth and strength of the weld. For small-scale projects involving thinner materials, a lower power output could suffice, while larger or more complex assemblies may necessitate higher power levels for proper fusion. It's also beneficial to assess the welder's duty cycle to ensure it can sustain the required work rate without overheating, as continuous operation can affect durability and welding consistency. By carefully evaluating these parameters, you can select an ultrasonic welder that meets your project's demands effectively.
| Feature | Description | Application | Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency | Typically between 20 kHz to 40 kHz | Ideal for plastics and thin materials | Efficient energy transfer for precise welding |
| Power Range | Varies from 100 W to 2000 W | Used in small-scale fabrications and repairs | Can handle small and intricate workpieces |
| Material Compatibility | Compatible with a variety of thermoplastics | Widely used in electronics, automotive, and medical sectors | Versatile application across many industries |
| Portability | Compact design for easy transport | Field repairs and onsite projects | Increased flexibility for project locations |
| Cooling System | Air or water-cooled options available | High-volume production environments | Prevents overheating during extended use |