Leave Your Message
In the realm of modern manufacturing, efficiency and precision are paramount. One of the innovative technologies that have emerged to meet these demands is the Ultrasonic Welder. This advanced piece of equipment utilizes high-frequency sound waves to create strong, durable bonds between materials, making it an essential tool in various industries, including automotive, electronics, and medical device manufacturing. The process it employs not only enhances the quality of the final product but also streamlines production timelines, thereby reducing operational costs.
The Ultrasonic Welder operates by converting electrical energy into mechanical vibrations through a transducer. These vibrations are then amplified and directed into the materials being joined, generating localized heating at the interface, which leads to melting and fusing without the need for traditional adhesives or heat sources. This method offers numerous advantages over conventional welding techniques, such as improved control over the weld process, reduced energy consumption, and the capability to join dissimilar materials seamlessly. Understanding how an Ultrasonic Welder functions and its impact on manufacturing processes unveils a crucial tool for industries striving for innovation and quality in their production lines.

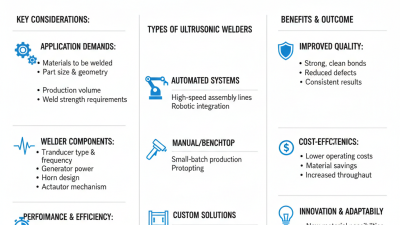
An ultrasonic welder is a sophisticated machine used in various manufacturing processes to join materials, primarily plastics and metals, without the need for adhesives, fasteners, or heat. It operates by utilizing high-frequency ultrasonic vibrations that create localized heat at the interface of the materials being joined. This heat melts the surfaces, allowing them to fuse together upon cooling, resulting in a strong and durable bond. The process is particularly advantageous in the automotive, medical, and electronics industries, where precision and efficiency are paramount.
When considering the implementation of ultrasonic welding in a manufacturing setting, it's essential to understand its functionality thoroughly. The machine comprises a generator that produces ultrasonic waves, a transducer that converts these waves into mechanical vibrations, and a sonotrode that applies pressure to the materials being welded. One significant benefit of this technique is its speed; it often requires mere seconds to complete a weld, significantly enhancing production rates.
Tips for effective ultrasonic welding include ensuring that surfaces to be joined are clean and free from contaminants, as even minor impurities can compromise the quality of the weld. Additionally, selecting the appropriate frequency and amplitude for the specific materials can optimize the welding process, leading to better results. Regular maintenance of the ultrasonic welder is also crucial, as it helps maintain performance and extends the lifespan of the equipment.
| Feature | Description | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency | Typically operates between 20 kHz and 40 kHz | Used in electronics, automotive, and medical devices |
| Welding Mechanism | Uses high-frequency ultrasonic vibrations to generate localized heat | Suitable for plastics, metals, and dissimilar materials |
| Advantages | Fast, energy-efficient, and produces strong welds | Ideal for high-volume production environments |
| Disadvantages | Initial equipment cost can be high; limited to small parts | Less effective for thicker materials |
| Common Materials | Thermoplastics, metals like aluminum, and composite materials | Widely used in packaging, automotive, and consumer goods |
| Control Systems | Modern systems use digital controls for precision and repeatability | Enhances quality control in manufacturing |
Ultrasonic welding is a critical technology in modern manufacturing, particularly in industries such as automotive, electronics, and medical devices. The process relies on precise components that work together to achieve efficient and effective bonding. Key components of ultrasonic welding machines include the ultrasonic generator, transducer, booster, and sonotrode. Each plays a vital role in converting electrical energy into mechanical vibrations, which can then be used to fuse materials together at a molecular level.
The ultrasonic generator creates high-frequency electrical signals, which are transformed into mechanical vibrations by the transducer. The booster amplifies these vibrations, allowing for greater force application at the welding site. Finally, the sonotrode, or welding horn, directs this energy precisely where it is needed, ensuring consistent and reliable welds. Industry reports indicate a growing demand for ultrasonic welding, with the global market expected to reach $2.5 billion by 2025, reflecting its significance in achieving efficiency and cost reduction in manufacturing processes.
As manufacturers continue to seek innovative solutions to enhance production capabilities, ultrasonic welding machines are becoming increasingly integral. Their ability to provide clean and fast welding without the need for additional materials or high temperatures makes them an ideal choice for assembling delicate components. According to a recent study, ultrasonic welding processes can increase production speed by up to 30%, showcasing their vital role in modern manufacturing settings.

Ultrasonic welding is a sophisticated method employed widely in modern manufacturing, leveraging high-frequency sound waves to join materials, typically plastics or metals, without the need for additional adhesives or mechanical fasteners. The process operates at frequencies typically between 20 kHz and 40 kHz, causing a rapid vibration that generates localized heat through friction at the joint interface. This unique approach provides a clean and efficient means of bonding, facilitating high production volumes and consistent quality in industrial applications.
According to a report by Grand View Research, the ultrasonic welding market is projected to reach approximately $4.6 billion by 2025, driven by its increasing adoption in various sectors such as automotive, electronics, and medical device manufacturing. The ability of ultrasonic welding to create strong, durable joints while minimizing energy consumption and waste is a significant advantage as industries strive for sustainability. Furthermore, studies indicate that ultrasonic welding can reduce assembly times by up to 50%, underscoring its importance in optimizing manufacturing processes in today's fast-paced environment. Such advancements highlight the growing reliance on ultrasonic technology to improve efficiency and performance in manufacturing operations.
Ultrasonic welding has revolutionized various industries by providing a fast and efficient method for joining materials, particularly plastics and metals. In automotive manufacturing, ultrasonic welding is commonly employed to assemble components such as dashboards, fuel tanks, and battery cases. This technique allows for strong, permanent bonds without the need for adhesives or mechanical fasteners, which can add weight and complexity to designs. The ability to weld complex geometries with precision makes it ideal for producing lightweight and durable automotive parts that meet stringent safety and performance standards.
In the medical device industry, ultrasonic welding is utilized to create secure seals in disposable products like syringes, IV bags, and surgical instruments. The process is favored for its cleanliness and minimal thermal impact on the components being joined, which is crucial in applications where sterility and material integrity are essential.
Additionally, ultrasonic welding is increasingly being adopted in electronics manufacturing, where it is used to join thin wires and components for circuit boards. This method enables precise and reliable connections while minimizing the risk of damage to sensitive parts, fostering advancements in the ever-evolving tech landscape.
Ultrasonic welding is gaining significant traction in modern manufacturing due to its distinctive advantages over traditional welding methods. One of the primary benefits is the speed and efficiency of the process. Ultrasonic welding utilizes high-frequency vibrations, which generates heat at the interface of the materials being joined. This results in quicker weld times, often completed in mere seconds, compared to conventional methods that may require more extensive heating and cooling phases. This enhanced speed not only increases production rates but also optimizes workflow and reduces energy consumption during the manufacturing process.
In addition to speed, ultrasonic welding is recognized for its ability to create strong, consistent, and reliable joints without the need for additional adhesives or fasteners. Traditional welding techniques often produce larger heat-affected zones, potentially compromising material integrity. However, ultrasonic welding localizes the heat generation, minimizing the thermal impact on surrounding areas and maintaining the overall strength of components. Furthermore, the precision of ultrasonic welding is particularly beneficial in industries requiring delicate assemblies, such as electronics and medical devices, where the risk of damaging components is a critical concern. This precision combined with reduced waste makes ultrasonic welding a preferred choice in many contemporary manufacturing applications.