Leave Your Message
Ultrasonic Welder Plastic is revolutionizing manufacturing processes across various industries. According to a recent report by MarketsandMarkets, the global ultrasonic welding market is projected to reach $3.5 billion by 2025. This growth underlines the increasing demand for efficient and reliable joining methods. Ultrasonic welding uses high-frequency sound waves to fuse plastic materials. The result is a strong, durable bond created without the need for adhesives.
Industries such as automotive, electronics, and medical devices are adopting this technology. The precision of ultrasonic welds contributes to product integrity. Yet, challenges remain in standardizing processes across different materials. Different plastics react differently to ultrasonic welding, which requires careful calibration of the welding parameters. Moreover, while ultrasonic welding is efficient, it may not be suitable for all applications, necessitating a thorough evaluation. Embracing Ultrasonic Welder Plastic can enhance manufacturing efficiency, but it's essential to recognize and address these complexities for optimal results.
Ultrasonic welding for plastics is a specialized process. It employs high-frequency ultrasonic vibrations to bond plastic parts. This technique is efficient and often used in various industries, from automotive to electronics. The process involves placing the parts together and applying ultrasonic energy, creating localized heat at the joint area. This heat melts the plastic, forming a strong bond once cooled.
The beauty of ultrasonic welding lies in its speed and precision. It can complete a bond in seconds. However, the method isn’t without its challenges. Factors like material compatibility and joint design significantly impact the weld's strength. Improper settings can lead to weak bonds or even damaged components. Experimentation and adjustment are often necessary to perfect the output.
Moreover, not all plastic materials respond well to ultrasonic welding. Some may require specific frequencies or additional aids to achieve effective bonding. It’s essential to understand these nuances. Each project may reveal its own set of challenges, prompting a need for reflection and adjustment in processes. Reducing waste and ensuring quality remain ongoing pursuits in this technology.
| Dimension | Detail |
|---|---|
| Welding Technology | Ultrasonic Welding |
| Frequency | 20 kHz to 40 kHz |
| Materials | Thermoplastics such as PP, PE, PS, and PVC |
| Process Type | Non-contact, mechanical welding |
| Heating Method | Frictional heat generated by ultrasonic waves |
| Speed | Seconds; typically 1-5 seconds |
| Advantages | Quick process, low energy consumption, strong joints |
| Applications | Automotive, electronics, medical devices, packaging |
| Limitations | Limited to certain plastics, requires precise alignment |
Ultrasonic welding is a fascinating technology that bonds plastics through high-frequency vibrations. The core principle revolves around converting electrical energy into mechanical vibrations. These vibrations create heat at the interface of the plastic parts, leading to melting and forming a strong joint. Reports indicate that ultrasonic welding offers a quick process, often taking less than one second for a complete weld. It is effective for various thermoplastics, making it essential in industries like automotive and medical devices.
Tips: Always consider the materials involved. Different plastics have unique requirements for optimal welding. Misalignment can cause defects. Understanding the material properties ensures a successful weld.
Ultrasonic welding stands out for its ability to produce strong, repeatable bonds. However, challenges exist. If the frequency is not suitable, it may lead to weak joints or material damage. Maintaining the right pressure and amplitude is crucial. Studies reveal that improper settings could affect bond strength by up to 30%. Continuous monitoring is essential to maintain quality and adapt to material changes.

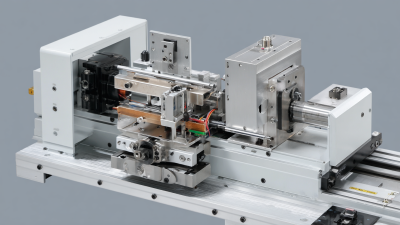
Ultrasonic welders are specialized machines used for joining plastic materials. Their effectiveness lies in several key components. The ultrasonic transducer is essential; it converts electrical energy into high-frequency sound waves. This process generates vibration. These vibrations create friction at the contact points of the plastics, which leads to melting and permits bonding.
Another critical part is the sonotrode. It amplifies the ultrasonic energy and directs it to the workpiece. The design of the sonotrode can vary significantly based on the application. A poorly designed sonotrode may lead to uneven heating, resulting in weak joints. Additionally, the fixture holds the plastic parts securely during the welding process. A flimsy fixture might cause misalignment, leading to insufficient weld quality.
Cooling systems are also vital. They help in solidifying the welded joint quickly. Without proper cooling, the joint may remain weak, causing products to fail under stress. Balancing the welding time and cooling time is challenging. Often, optimizing these aspects requires trial and error. Each adjustment provides valuable feedback for future welds, offering room for improvement.
Ultrasonic welding of plastics is an efficient and innovative process. It uses high-frequency sound waves to join materials at the molecular level. The method is quick, typically taking just seconds to create strong welds. The process consists of several steps that are crucial for success.
First, the plastic parts are placed in the welding fixture. This positioning is critical; improper alignment can lead to weak joints. Next, ultrasonic vibrations are applied to the interface of the parts. These vibrations generate heat through friction. The heat melts the plastic at the weld area, creating a bond as the materials cool down.
After the weld is complete, it’s important to inspect the joint. Sometimes, the weld may appear strong but lacks durability. This is where quality control plays a vital role. Minor adjustments in pressure or time can lead to better results. Continuous testing and tweaking are essential for optimal performance. Ultrasonic welding has a learning curve, and mastery comes from practice and experience.
Ultrasonic plastic welding is a fast and efficient method of joining plastic materials. This technology uses high-frequency sound waves to create vibrations. These vibrations generate heat at the joint interface. As a result, the plastic melts and forms a strong bond. This technique is widely used across various industries including automotive, medical, and electronics. In fact, industry reports indicate that the ultrasonic welding market is projected to grow at a CAGR of around 7% through the next five years.
The benefits of ultrasonic plastic welding are significant. First, it offers a clean bonding process without the need for adhesives or additional materials. This can lead to cost savings and reduced waste. Moreover, the bonds created are strong and reliable, essential for product integrity in critical applications. Interestingly, the process allows for various shapes and types of plastics to be welded, increasing its versatility.
Tips: Always ensure that the materials are compatible for ultrasonic welding. Some plastics may require specific settings. Additionally, during the design phase, consider the joint geometry. Sometimes, common designs lead to weaker bonds. It’s crucial to evaluate and refine designs based on performance data. Not every method will work perfectly for every application, so ongoing testing is essential.