Leave Your Message
An Ultrasonic Wire Welder is a specialized device used in various manufacturing processes. It utilizes high-frequency ultrasonic waves to join wires and metal components together. This technology is critical in industries like electronics and automotive manufacturing, where precision is essential.
The Ultrasonic Wire Welder operates by applying ultrasonic vibrations to the materials being joined. The friction generated by these vibrations creates heat, which allows the metals to bond effectively. This method ensures strong and reliable connections without the need for additional materials or heat sources.
While this technology brings many benefits, there are challenges to consider. Not all materials are suitable for ultrasonic welding. Some metals may not bond well, leading to weak connections. Additionally, the initial setup and calibration can be complex, requiring skilled operators. Understanding these aspects is crucial for optimal performance and longevity in the welding process.

Ultrasonic wire welders are innovative tools used in various industries. They utilize high-frequency sound waves to join metal materials. This process is often used for connecting fine wires or delicate components. Unlike traditional welding, ultrasonic welding does not require high temperatures. Instead, it creates localized melting through vibrations. This method is efficient and produces strong bonds.
The operation involves a transducer that converts electrical energy into mechanical vibrations. These vibrations are applied to the wires for a brief time. As the surfaces come together, heat builds up at the contact points. It allows the metals to fuse effectively without compromising their integrity. The precision of this technique is noteworthy, yet it requires careful setup. Slight misalignment can affect the weld quality.
While ultrasonic welding is advantageous, it may not be suitable for all applications. Some materials do not respond well to this method. Additionally, the equipment requires regular maintenance to function optimally. Over time, components can wear down, resulting in inconsistent results. As industries evolve, it is essential to continually evaluate the effectiveness of ultrasonic welding in specific applications.
Ultrasonic welding technology is a fascinating method used in various industries. It relies on high-frequency sound waves to join materials together. The basic principle involves creating localized heat through ultrasonic vibrations. This heat causes the surfaces of the materials to soften, allowing them to bond.
In practical application, ultrasonic welders can join thermoplastics and thin metals efficiently. Reports show that this technology can improve production speeds by 30% compared to traditional welding methods. However, precision is crucial. Improper settings can lead to inconsistent welds. Each material type requires specific frequency adjustments for optimal results.
Tips: Always calibrate your equipment before use. Regular maintenance can prevent wear and tear.
The power of ultrasonic welding lies in its ability to produce strong joints without additional adhesives. This means cleaner processes and reduced environmental impact. Yet, relying too heavily on this method can pose challenges during the transition between materials. Factors like material thickness and surface texture must be monitored closely to avoid mistakes.
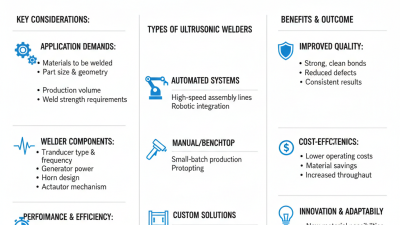
Ultrasonic wire welders play a crucial role in modern manufacturing. They join materials using high-frequency sound waves. Understanding the components of these welders helps maximize their efficiency.
A typical ultrasonic wire welder comprises a few key parts: the ultrasonic generator, transducer, sonotrode, and the anvil. The ultrasonic generator converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. It emits a signal that powers the transducer. The transducer then vibrates at ultrasonic frequencies. This vibration is responsible for heating the materials to be welded.
The sonotrode, often made of titanium or aluminum, focuses these vibrations onto the wire. The anvil provides a stable base for the assembly. Recent industry reports indicate that ultrasonic welding can increase production speed by up to 50%. However, it requires precise control of parameters. Inadequate adjustments can lead to weak welds, which could compromise product integrity. The balance between speed and strength remains a challenge for many manufacturers. Achieving optimal results often calls for careful experimentation and thorough quality checks.
Ultrasonic wire welding is a complex yet fascinating process that plays a vital role in various industries. The process begins with the alignment of wire to be welded. The wires are placed under a specific pressure, ensuring they are tightly arranged. This is crucial for achieving optimal results.
Next, the ultrasonic welding machine generates high-frequency vibrations through the transducer. These vibrations are transmitted to the workpieces. As the vibrations increase, the friction generates heat. This heat is essential for melting the wire surfaces, allowing them to fuse together seamlessly. Industry reports indicate that ultrasonic welding can achieve bond strengths of over 90% of the wire's original strength.
After the bonding, the process requires careful cooling. Cooling is important to ensure the newly formed weld maintains its integrity. This step involves a precise timing mechanism. If not monitored, the weld may become weak or unusable. Despite being efficient, issues can arise, such as inadequate pressure or poor wire alignment. These factors should always be considered to ensure high-quality welds. The process is intricate, and slight missteps can lead to significant impacts on overall performance.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | An ultrasonic wire welder is a device that uses high-frequency sound waves to create a bond between wires through a process called ultrasonic welding. |
| Working Principle | The welder generates ultrasonic vibrations which cause localized melting at the interface of the wires, resulting in a solid-state bond. |
| Equipment Components | Key components include a generator, transducer, booster, sonotrode, and tooling fixtures. |
| Applications | Commonly used in industries such as automotive, electronics, and medical devices for connecting wires. |
| Advantages | Offers fast processing times, minimal thermal damage, and high-quality welds without the need for adhesives. |
| Limitations | Not suitable for thick materials or certain metal types; requires precise control and setup. |
| Step-by-Step Process |
1. Preparation of wires 2. Positioning in the tooling fixtures 3. Activation of ultrasonic vibrations 4. Formation of the weld 5. Cooling and inspection |
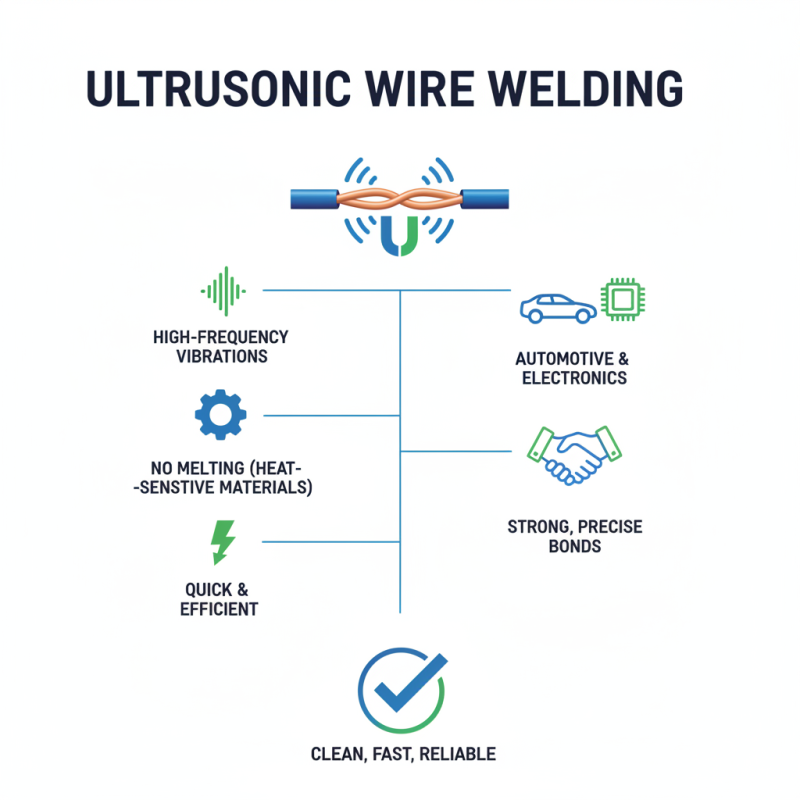
Ultrasonic wire welding is a unique joining technique. It uses high-frequency ultrasonic vibrations to create a strong bond between wires. This method is widely applied in various industries, especially automotive and electronics. It enables precise and efficient connections. Wires can be bonded quickly without melting them. This is crucial when dealing with heat-sensitive materials.
One major benefit is the reduction of production time. Ultrasonic welding dramatically speeds up the manufacturing process. This can lead to higher operational efficiency for companies. Additionally, it minimizes the use of adhesives. This can result in a cleaner and safer working environment. However, not every application may be suitable for this method. Some materials might not bond well using ultrasonic technology, requiring further investigation.
The versatility of ultrasonic wire welding opens many doors. It can be used for different materials and wire sizes. This adaptability allows manufacturers to tailor their processes. However, challenges remain, such as equipment costs and training needs. Careful consideration is vital for successful implementation.